Glen’s recent busy project, the demand is a bit chaotic, tonight I used the demand analysis artifact Kano model to sort it out, and the whole person is much better. When you are faced with a lot of demand points, how to do subtraction? Use the Kano model, it can effectively help you sort out product demand points and improve efficiency.
The Kano model helps you analyze the importance of your needs
When designing any product, product managers will always encounter many key requirements. If these points are not sorted out clearly, the project will definitely (very sure tone) eventually go wrong.
Resources are always limited
Any Internet product, even the simplest activity page, will involve a lot of requirements, and each requirement will lead to related functional logic. When there are many requirements, especially when many requirements are cross-covered, the logic of the product will change. It’s very complicated.
The resources for developing products are often limited, and you often find that there is always insufficient manpower for development, design, and testing. Therefore, the basic requirement for product managers is to refine the correct and effective requirements by optimizing product design based on limited resources, and try to avoid temporary changes in requirements during subsequent design and development, at least to achieve framework-level requirements Not much changed. (Recently, due to the mistakes of our product team, a front-end girl worked late at night, and my heart is very disturbed.)
What is the Kano model?
The Kano model is also called the Kano Model, which was proposed in 1984 by the Japanese quality control master Dr. Noriaki Kano. The core of the Kano model is to divide product quality into 5 parts:
- A Indifference: Whether this quality is provided or not, user satisfaction will not change. In other words, users do not care about this quality at all; this quality needs to be avoided in product design.
- B. Attractive quality (Attractive): The quality that users can’t imagine. If this quality is not provided, user satisfaction will not be reduced. Once the attractive quality is provided, user satisfaction will be greatly improved.
- C One-dimensional quality (One-dimensional): One-dimensional quality is also known as linear quality. If the quality is good, the customer satisfaction is high. On the contrary, if the quality is poor, the customer will give negative comments.
- D. Must-be: This is the basic requirement of the product. No matter how the necessary quality is improved, customers will have an upper limit of satisfaction, but if this requirement is not provided, user satisfaction will be greatly reduced.
- E Reverse quality (Reverse): Users do not have this demand at all, and user satisfaction will decline after providing it.
The relationship between several qualities of the Kano model is as follows:
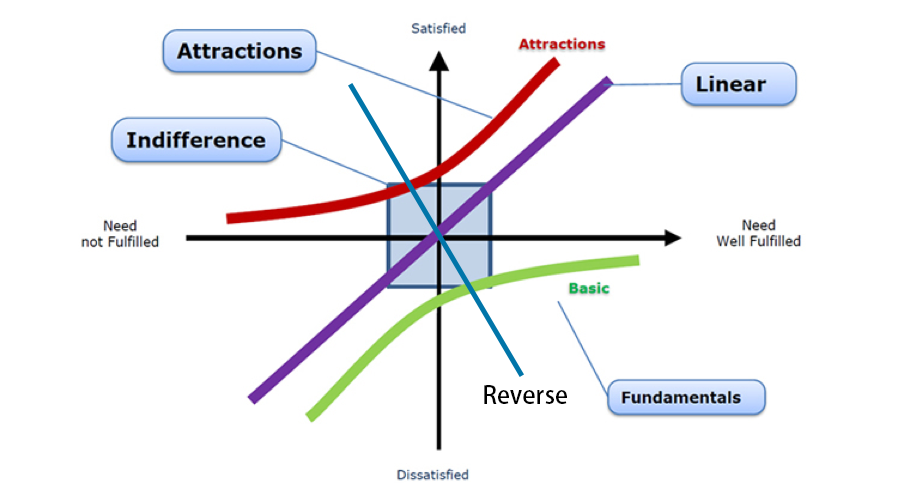
Use Kano model to distinguish product demand
The above briefly mentioned several qualities. When we design products, we need to avoid indifferent quality and reverse quality as much as possible, at least do the necessary quality, one-dimensional quality, and strive to be attractive quality.
- Try to avoid: indifferent quality, reverse quality
- Do at least: necessary quality, one-dimensional quality
- Try to do it well: Charismatic quality
When analyzing product demand points, analyze all the determined needs and evaluate them according to: like, as it should be, indifferent, tolerable, and dislike. Then, according to the table below, find out what type each requirement belongs to.
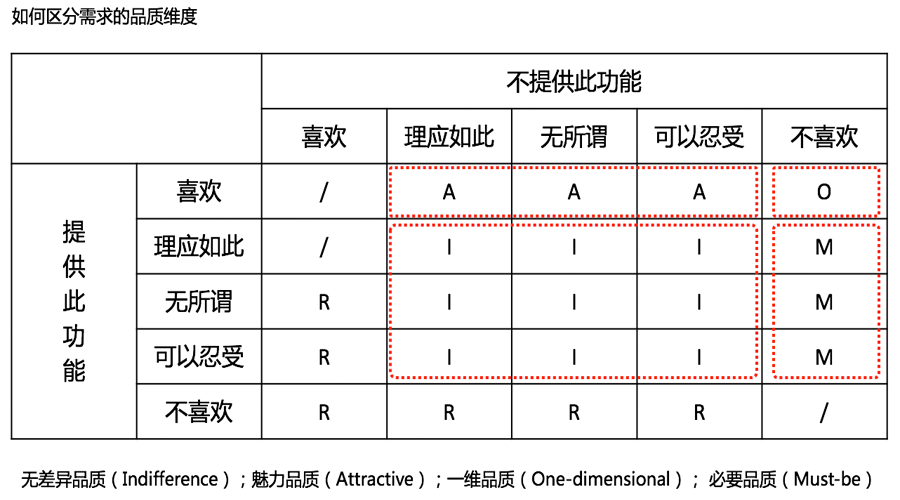
Then, the product manager has to write the product requirement document according to the stage of the product, and then can go to the development and design of children’s shoes to enter the product development work. I believe that after you sort out the requirements yourself, you will be more confident and firm when you go to the development and design review.
Carnot model application examples
Now that the weather is cold, everyone should start to eat hot pot. This time we will take hot pot as an example and use the Kano model in actual combat. We remove the reverse quality and simplify the analysis process.
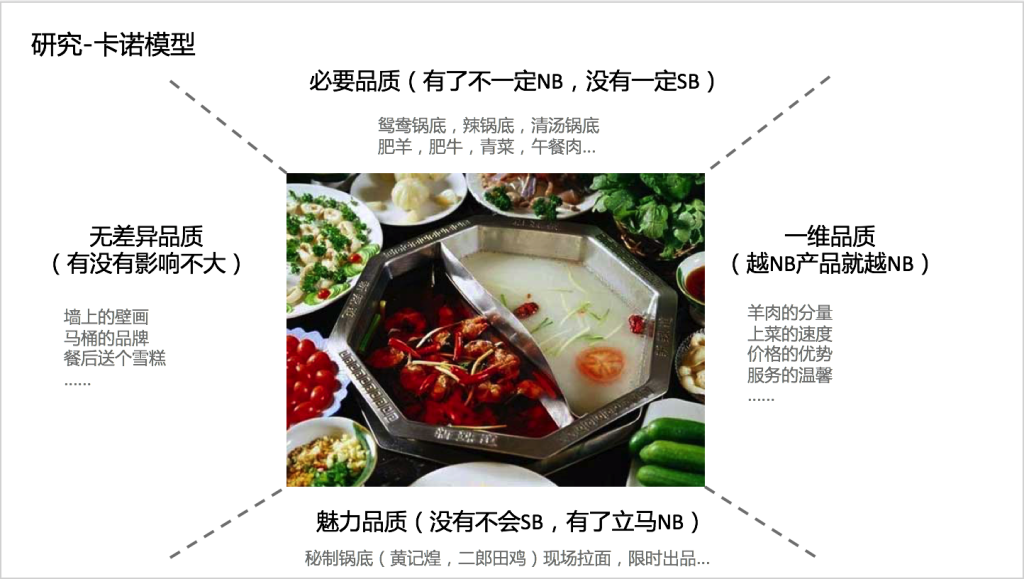
- Necessary quality (not necessarily NB, not certain SB): The necessary quality must be possessed. A hot pot meal requires at least the bottom of the pot and a few classic dishes.
- One-dimensional quality (the more NB the product is, the more NB the product is): The better the one-dimensional quality is, the better the product will be. This is the factor that determines the linear quality of the product; when eating hot pot, the weight of the dish and the store’s service are well done , Can effectively improve product quality.
- Charm quality (no SB, with Lima NB): Charm quality is equivalent to an innovation. With enough charisma quality, your product will be distinguished from other similar products; Haidilao will give you a reward when you eat hot pot. You polish your shoes, which belongs to the quality of charm.
- Undifferentiated quality (whether or not it has little effect): Indifferent quality is the same as without, for example, you put a few books in a hot pot restaurant. . .
That’s it, good night.
Thanks for reading!
